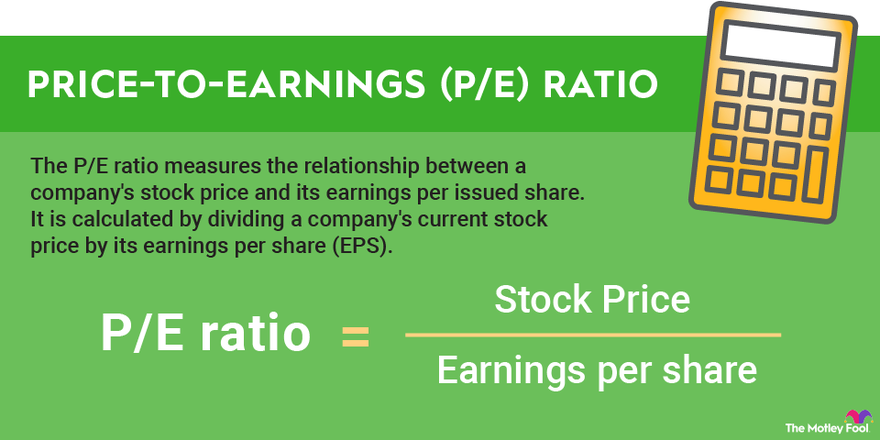
Price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) is a popular stock valuation method that compares a company’s stock price to its earnings. It helps investors determine how much they are paying for each dollar of earnings. If you’re new to investing or want to learn more about this important financial concept, you’re in the right place.
Other than P/E ratio, there are various stock valuation methods that investors can use to assess the worth of a company and make informed investment decisions. Let’s explore some of them:
Price-to-Book (PB) Ratio
The price-to-book (PB) ratio compares a company’s market value to its book value. It helps investors assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its accounting value. To learn more about PB ratio and its calculation, read our article: Price-to-Book Ratio Definition, Formula, and Examples.
Price/Earnings-to-Growth (PEG) Ratio
The price/earnings-to-growth (PEG) ratio ties a company’s P/E ratio to its earnings growth rate. It helps investors identify stocks that might be undervalued or overvalued based on their growth potential. To understand how to calculate and interpret the PEG ratio, check out our guide: Price/Earnings-to-Growth (PEG) Ratio: What It Is and How to Use It.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis estimates the intrinsic value of a stock by calculating the present value of its expected future cash flows. This valuation method is widely used by investors to determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued. Learn more about DCF analysis and how to apply it in our comprehensive guide: Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Explained With Formula and Examples.
Relative Valuation Model
Relative valuation compares a company’s financial metrics, such as P/E ratio or PB ratio, to similar companies in the same industry. It helps investors evaluate whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued compared to its peers. Check out our article on the topic to learn more: The Comparables Approach to Equity Valuation.
Determining Intrinsic Value
Intrinsic value is the estimated true value of a stock based on its expected future cash flows. Understanding how to calculate intrinsic value using different formulas, such as discounted cash flow analysis, is essential for investors. Read our in-depth guide to learn more: Intrinsic Value of Stock: What It Is and How to Calculate It.
Conclusion
Now that you have a better understanding of different stock valuation methods such as P/E ratio, PB ratio, PEG ratio, DCF analysis, and relative valuation, you can make more informed investment decisions. Remember, no single method is foolproof, and it’s essential to consider various factors when evaluating stocks. Happy investing!
Other references:
Leave a Reply